9.6 KiB
AWS Cloud Infrastructure Provisioning
Kubernetes can be installed just about anywhere physical or virtual machines can be run. In this lab we are going to focus on Amazon EC2 (IaaS).
This lab will walk you through provisioning the compute instances required for running a H/A Kubernetes cluster. A total of 9 virtual machines will be created.
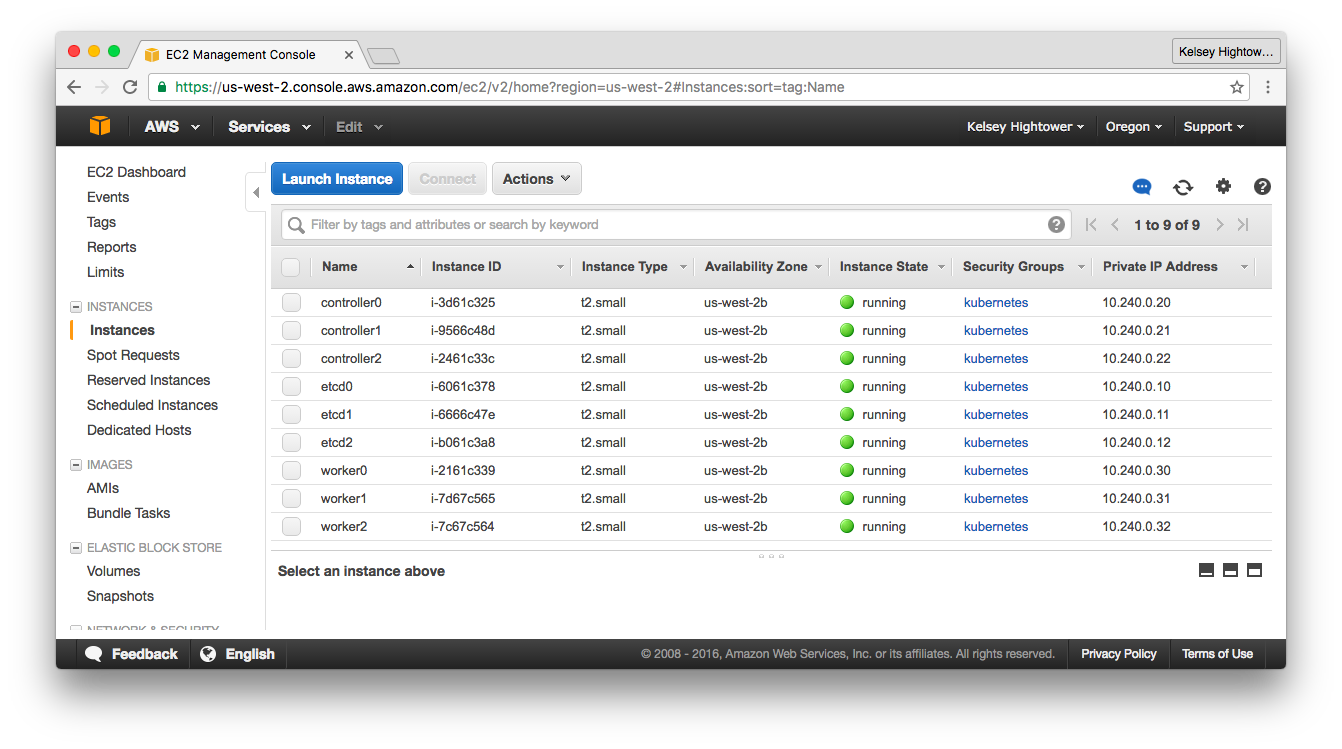
After completing this guide you should have the following compute instances:
All machines will be provisioned with fixed private IP addresses to simplify the bootstrap process.
To make our Kubernetes control plane remotely accessible, a public IP address will be provisioned and assigned to a Load Balancer that will sit in front of the 3 Kubernetes controllers.
Create a Custom Network
VPC_ID=$(aws ec2 create-vpc \
--cidr-block 10.240.0.0/16 | \
jq -r '.Vpc.VpcId')
aws ec2 modify-vpc-attribute \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID} \
--enable-dns-support '{"Value": true}'
aws ec2 modify-vpc-attribute \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID} \
--enable-dns-hostnames '{"Value": true}'
DHCP_OPTION_SET_ID=$(aws ec2 create-dhcp-options \
--dhcp-configuration "Key=domain-name,Values=us-west-2.compute.internal" \
"Key=domain-name-servers,Values=AmazonProvidedDNS" | \
jq -r '.DhcpOptions.DhcpOptionsId')
aws ec2 associate-dhcp-options \
--dhcp-options-id ${DHCP_OPTION_SET_ID} \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID}
Create a subnet for the Kubernetes cluster:
SUBNET_ID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID} \
--cidr-block 10.240.0.0/24 | \
jq -r '.Subnet.SubnetId')
Create an internet gateway
INTERNET_GATEWAY_ID=$(aws ec2 create-internet-gateway | \
jq -r '.InternetGateway.InternetGatewayId')
aws ec2 attach-internet-gateway \
--internet-gateway-id ${INTERNET_GATEWAY_ID} \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID}
Route Table
ROUTE_TABLE_ID=$(aws ec2 create-route-table \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID} | \
jq -r '.RouteTable.RouteTableId')
aws ec2 associate-route-table \
--route-table-id ${ROUTE_TABLE_ID} \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID}
aws ec2 create-route \
--route-table-id ${ROUTE_TABLE_ID} \
--destination-cidr-block 0.0.0.0/0 \
--gateway-id ${INTERNET_GATEWAY_ID}
Firewall Rules
SECURITY_GROUP_ID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group \
--group-name kubernetes \
--description "Kubernetes security group" \
--vpc-id ${VPC_ID} | \
jq -r '.GroupId')
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--protocol all
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--protocol tcp \
--port 22 \
--cidr 0.0.0.0/0
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--protocol tcp \
--port 443 \
--cidr 0.0.0.0/0
Create the Kubernetes Public IP Address
Create a public IP address that will be used by remote clients to connect to the Kubernetes control plane:
KUBERNETES_PUBLIC_IP=$(aws ec2 allocate-address \
--domain vpc | \
jq -r '.PublicIp')
Provision Virtual Machines
All the VMs in this lab will be provisioned using Ubuntu 16.04 mainly because it runs a newish Linux Kernel that has good support for Docker.
Create Instance IAM Policies
cat > kubernetes-iam-role.json <<'EOF'
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{"Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"}, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole"}
]
}
EOF
aws iam create-role \
--role-name kubernetes \
--assume-role-policy-document file://kubernetes-iam-role.json
cat > kubernetes-iam-policy.json <<'EOF'
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{"Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["ec2:*"], "Resource": ["*"]},
{"Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["elasticloadbalancing:*"], "Resource": ["*"]},
{"Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["route53:*"], "Resource": ["*"]},
{"Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["ecr:*"], "Resource": "*"}
]
}
EOF
aws iam put-role-policy \
--role-name kubernetes \
--policy-name kubernetes \
--policy-document file://kubernetes-iam-policy.json
aws iam create-instance-profile \
--instance-profile-name kubernetes
aws iam add-role-to-instance-profile \
--instance-profile-name kubernetes \
--role-name kubernetes
Chosing an Image
Use the Ubuntu Amazon EC2 AMI Locator to find the right image-id for your zone. This guide assumes the us-west-2 zone.
IMAGE_ID="ami-746aba14"
Generate A SSH Key Pair
aws ec2 create-key-pair --key-name kubernetes | \
jq -r '.KeyMaterial' > ~/.ssh/kubernetes_the_hard_way
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/kubernetes_the_hard_way
ssh-add ~/.ssh/kubernetes_the_hard_way
etcd
ETCD_0_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.10 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${ETCD_0_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=etcd0
ETCD_1_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.11 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${ETCD_1_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=etcd1
ETCD_2_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.12 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${ETCD_2_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=etcd2
Kubernetes Controllers
CONTROLLER_0_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--iam-instance-profile 'Name=kubernetes' \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.20 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${CONTROLLER_0_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=controller0
CONTROLLER_1_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--iam-instance-profile 'Name=kubernetes' \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.21 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${CONTROLLER_1_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=controller1
CONTROLLER_2_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--iam-instance-profile 'Name=kubernetes' \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.22 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${CONTROLLER_2_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=controller2
Kubernetes Workers
WORKER_0_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--iam-instance-profile 'Name=kubernetes' \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.30 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${WORKER_0_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=worker0
WORKER_1_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--iam-instance-profile 'Name=kubernetes' \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.31 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${WORKER_1_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=worker1
WORKER_2_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--iam-instance-profile 'Name=kubernetes' \
--image-id ${IMAGE_ID} \
--count 1 \
--key-name kubernetes \
--security-group-ids ${SECURITY_GROUP_ID} \
--instance-type t2.small \
--private-ip-address 10.240.0.32 \
--subnet-id ${SUBNET_ID} | \
jq -r '.Instances[].InstanceId')
aws ec2 create-tags \
--resources ${WORKER_2_INSTANCE_ID} \
--tags Key=Name,Value=worker2
Verify
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" | \
jq -j '.Reservations[].Instances[] | .InstanceId, " ", .Placement.AvailabilityZone, " ", .PrivateIpAddress, " ", .PublicIpAddress, "\n"'
i-f3714f2e us-west-2c 10.240.0.22 XX.XXX.XX.XX
i-ae714f73 us-west-2c 10.240.0.11 XX.XX.XX.XXX
i-f4714f29 us-west-2c 10.240.0.21 XX.XX.XXX.XXX
i-f6714f2b us-west-2c 10.240.0.12 XX.XX.XX.XX
i-e26e503f us-west-2c 10.240.0.30 XX.XX.XXX.XXX
i-e36e503e us-west-2c 10.240.0.31 XX.XX.XX.XX
i-e8714f35 us-west-2c 10.240.0.10 XX.XX.XXX.XXX
i-78704ea5 us-west-2c 10.240.0.20 XX.XX.XXX.XXX
i-4a6e5097 us-west-2c 10.240.0.32 XX.XX.XX.XX