7.1 KiB
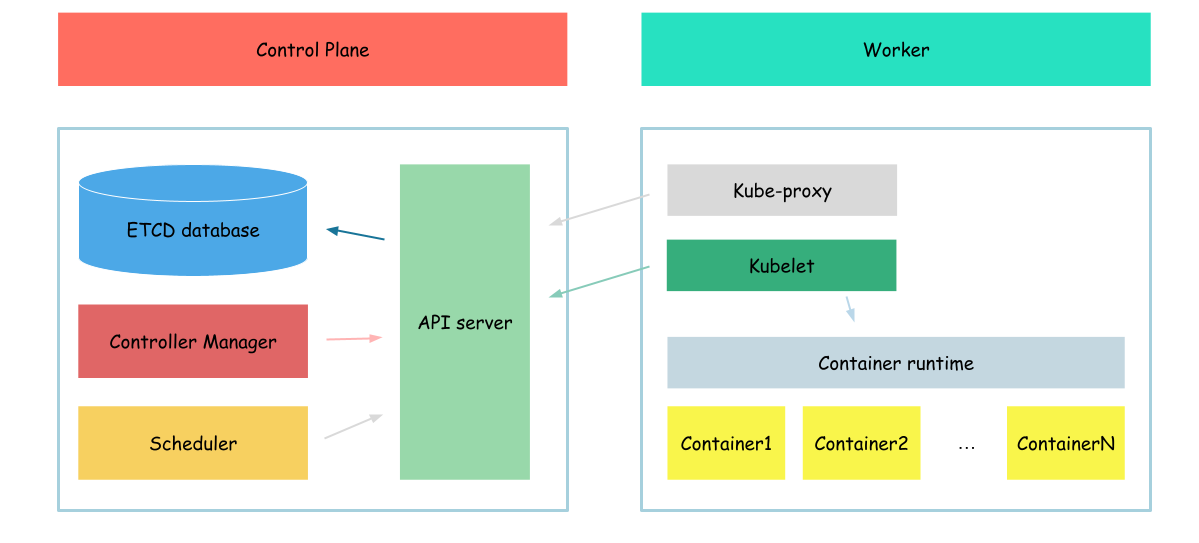
Controller manager
In this section we will configure controller-manager.
Controller Manager is a core component responsible for managing various controllers that regulate the desired state of the cluster. It runs as a separate process on the Kubernetes control plane and includes several built-in controllers
To see controller manager in action, we will create deployment before controller manager configured.
{
cat <<EOF> deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world-deployment
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world-deployment
spec:
serviceAccountName: hello-world
containers:
- name: hello-world-container
image: busybox
command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do echo "Hello, World from deployment!"; sleep 1; done']
EOF
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
}
Check created deployment status:
kubectl get deploy
Output:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-deployment 0/1 0 0 24s
As we can se our deployment isn't in ready state.
As we already mentioned, in kubernetes controller manager is responsible to ensure that desired state of the cluster equals to the actual state. In our case it means that deployment controller should create replicaset and replicaset controller should create pod which will be assigned to nodes by scheduler. But as controller manager is not configured - nothing happen with created deployment.
So, lets configure controller manager.
certificates
We will start with certificates.
As you remeber we configured our API server cto use client certificate to authenticate user. So, lets create proper certificate for the controller manager
{
cat > kube-controller-manager-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "system:kube-controller-manager",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "Portland",
"O": "system:kube-controller-manager",
"OU": "Kubernetes The Hard Way",
"ST": "Oregon"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert \
-ca=ca.pem \
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
-config=ca-config.json \
-profile=kubernetes \
kube-controller-manager-csr.json | cfssljson -bare kube-controller-manager
}
Created certs:
kube-controller-manager.csr
kube-controller-manager-key.pem
kube-controller-manager.pem
The most interesting configuration options:
- cn(common name) - value, api server will use as a client name during authorization
- o(organozation) - user group controller manager will use during authorization
We specified "system:kube-controller-manager" in the organization. It says api server that the client who uses which certificate belongs to the system:kube-controller-manager group.
Now, we will distribute ca certificate, this ????
sudo cp ca-key.pem /var/lib/kubernetes/
configuration
After the certificate files created we can create configuration files for the controller manager.
{
kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--certificate-authority=ca.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--server=https://127.0.0.1:6443 \
--kubeconfig=kube-controller-manager.kubeconfig
kubectl config set-credentials system:kube-controller-manager \
--client-certificate=kube-controller-manager.pem \
--client-key=kube-controller-manager-key.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--kubeconfig=kube-controller-manager.kubeconfig
kubectl config set-context default \
--cluster=kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--user=system:kube-controller-manager \
--kubeconfig=kube-controller-manager.kubeconfig
kubectl config use-context default --kubeconfig=kube-controller-manager.kubeconfig
}
We created kubernetes configuration file, which says controller manager where api server is configured and which certificates to use communicating with it
Now, we can distribute created configuration file.
sudo mv kube-controller-manager.kubeconfig /var/lib/kubernetes/
After all required configuration file created, we need to download controller manager binaries.
wget -q --show-progress --https-only --timestamping \
"https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.21.0/bin/linux/amd64/kube-controller-manager"
And install it
{
chmod +x kube-controller-manager
sudo mv kube-controller-manager /usr/local/bin/
}
Now, we can create configuration file for controller manager service
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/kube-controller-manager.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Controller Manager
Documentation=https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/kube-controller-manager \\
--bind-address=0.0.0.0 \\
--cluster-cidr=10.200.0.0/16 \\
--cluster-name=kubernetes \\
--cluster-signing-cert-file=/var/lib/kubernetes/ca.pem \\
--cluster-signing-key-file=/var/lib/kubernetes/ca-key.pem \\
--kubeconfig=/var/lib/kubernetes/kube-controller-manager.kubeconfig \\
--leader-elect=true \\
--root-ca-file=/var/lib/kubernetes/ca.pem \\
--service-account-private-key-file=/var/lib/kubernetes/service-account-key.pem \\
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.32.0.0/24 \\
--use-service-account-credentials=true \\
--v=2
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
After configuration file created, we can start controller manager
{
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable kube-controller-manager
sudo systemctl start kube-controller-manager
}
And finaly we can check controller manadger status
sudo systemctl status kube-controller-manager
Output:
● kube-controller-manager.service - Kubernetes Controller Manager
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/kube-controller-manager.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-04-20 11:48:41 UTC; 30s ago
Docs: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
Main PID: 14805 (kube-controller)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 2275)
Memory: 32.0M
CGroup: /system.slice/kube-controller-manager.service
└─14805 /usr/local/bin/kube-controller-manager --bind-address=0.0.0.0 --cluster-cidr=10.200.0.0/16 --cluster-name=kubernetes --cluster-signing-cert-file=/var/lib/kubernetes/c>
...
As you can see our controller manager is up and running. So we can continue with our deployment.
kubectl get deploy
Output:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment 1/1 1 1 2m8s
As you can see our deployment is up anr running, all desired pods are also in running state
kubectl get pods
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
deployment-74fc7cdd68-89rqw 1/1 Running 0 67s
Now, when our controller manager configured, lets clean up our workspace.
kubectl delete -f deployment.yaml
Check if pod created by deployment deleted
kubectl get pod
Outpput:
No resources found in default namespace.
Next: Kube-proxy