7.2 KiB
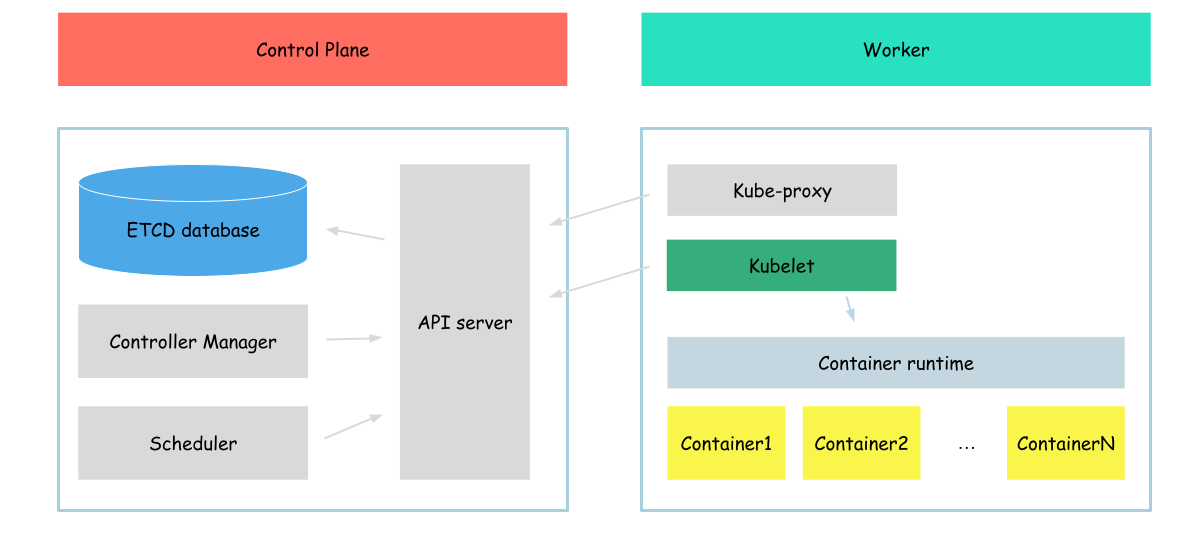
ETCD
At this point, we already know that we can run pods even without an API server. To create a pod we need to place some manifest in some place. It is not very comfortable to manage. Now we will start configuring "real" (more real than current, because current doesn't look like kubernetes at all) kubernetes cluster.
For kubernetes (at least for the original one if I can say so) we need to configure a database called etcd.
etcd is a strongly consistent, distributed key-value store that provides a reliable way to store data that needs to be accessed by a distributed system or cluster of machines. It gracefully handles leader elections during network partitions and can tolerate machine failure, even in the leader node.
Our etcd will be configured as a single node database with authentication.
So, let's start.
certificates
We will configure etcd to authenticate users by the certificate file used during communication. To do so, we need to generate some certs. We will create certificate files using cfssl and cfssljson tools (that should be installed before we start)
First of all, we will download the tools mentioned
wget -q --show-progress --https-only --timestamping \
https://github.com/cloudflare/cfssl/releases/download/v1.4.1/cfssl_1.4.1_linux_amd64 \
https://github.com/cloudflare/cfssl/releases/download/v1.4.1/cfssljson_1.4.1_linux_amd64
And install them
{
mv cfssl_1.4.1_linux_amd64 cfssl
mv cfssljson_1.4.1_linux_amd64 cfssljson
chmod +x cfssl cfssljson
sudo mv cfssl cfssljson /usr/local/bin/
}
After the tools are installed successfully, we need to generate ca certificate.
A ca (Certificate Authority) certificate, also known as a root certificate or a trusted root certificate, is a digital certificate that is used to verify the authenticity of other certificates.
{
cat > ca-config.json <<EOF
{
"signing": {
"default": {
"expiry": "8760h"
},
"profiles": {
"kubernetes": {
"usages": ["signing", "key encipherment", "server auth", "client auth"],
"expiry": "8760h"
}
}
}
}
EOF
cat > ca-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "Kubernetes",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "Portland",
"O": "Kubernetes",
"OU": "CA",
"ST": "Oregon"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca
}
Generated files:
ca-key.pem
ca.csr
ca.pem
Now, we can create certificate files signed by our ca file.
to simplify our kubernetes deployment, we will use this certificate for other kubernetes components as well, that is why we will add some extra configs (like KUBERNETES_HOST_NAME to it)
{
HOST_NAME=$(hostname -a)
KUBERNETES_HOSTNAMES=kubernetes,kubernetes.default,kubernetes.default.svc,kubernetes.default.svc.cluster,kubernetes.svc.cluster.local
cat > kubernetes-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "kubernetes",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "Portland",
"O": "Kubernetes",
"OU": "Kubernetes The Hard Way",
"ST": "Oregon"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert \
-ca=ca.pem \
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
-config=ca-config.json \
-hostname=worker,127.0.0.1,${KUBERNETES_HOSTNAMES},10.32.0.1 \
-profile=kubernetes \
kubernetes-csr.json | cfssljson -bare kubernetes
}
Generated files:
kubernetes.csr
kubernetes-key.pem
kubernetes.pem
And distribute certificate files created
{
sudo mkdir -p /etc/etcd /var/lib/etcd
sudo chmod 700 /var/lib/etcd
sudo cp ca.pem \
kubernetes.pem kubernetes-key.pem \
/etc/etcd/
}
configure
Now, we have all the required certificates, so, let's download etcd
wget -q --show-progress --https-only --timestamping \
"https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/releases/download/v3.4.15/etcd-v3.4.15-linux-amd64.tar.gz"
After the download is complete, we can move etcd binaries to the proper folders
{
tar -xvf etcd-v3.4.15-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv etcd-v3.4.15-linux-amd64/etcd* /usr/local/bin/
}
Now, we can configure etcd service
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/etcd.service
[Unit]
Description=etcd
Documentation=https://github.com/coreos
[Service]
Type=notify
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/etcd \\
--client-cert-auth \\
--name etcd \\
--cert-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes.pem \\
--key-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes-key.pem \\
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ca.pem \\
--listen-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:2379 \\
--advertise-client-urls https://127.0.0.1:2379 \\
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
Configuration options specified:
- client-cert-auth - this configuration option tels etcd to enable the authentication of clients using SSL/TLS client certificates. When client-cert-auth is enabled, etcd requires that clients authenticate themselves by presenting a valid SSL/TLS client certificate during the TLS handshake. This certificate must be signed by a trusted certificate authority (CA) and include the client's identity information
- name - used to specify the unique name of an etcd member
- cert-file - path to the SSL/TLS certificate file that the etcd server presents to clients during the TLS handshake
- key-file - path to the SSL/TLS private key file that corresponds to the SSL/TLS certificate presented by the etcd server during the TLS handshake
- trusted-ca-file - path to the ca file which will be used by etcd to validate client certificate
- listen-client-urls - specifies the network addresses on which the etcd server listens for client requests
- advertise-client-urls - specifies the network addresses that the etcd server advertises to clients for connecting to the server
- data-dir - directory where etcd stores its data, including the key-value pairs in the etcd key-value store, snapshots, and transaction logs
And finally, we need to run our etcd service
{
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable etcd
sudo systemctl start etcd
}
To ensure that our service successfully started, run
systemctl status etcd
Output:
● etcd.service - etcd
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/etcd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-04-20 10:55:03 UTC; 18s ago
Docs: https://github.com/coreos
Main PID: 12374 (etcd)
Tasks: 10 (limit: 2275)
Memory: 4.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/etcd.service
└─12374 /usr/local/bin/etcd --name etcd --cert-file=/etc/etcd/kubernetes.pem --key-file=/etc/
...
verify
When etcd is up and running, we can check whether we can communicate with it
sudo ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl member list \
--endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/etcd/ca.pem \
--cert=/etc/etcd/kubernetes.pem \
--key=/etc/etcd/kubernetes-key.pem
Output:
8e9e05c52164694d, started, etcd, http://localhost:2380, https://127.0.0.1:2379, false
As you can see, to communicate with the etcd service, we specified a cert and key file, this is the same file we used to configure etcd, it is only to simplify our deployment, in real life, we can use a different certificate which is signed by the same ca file.
Next: Api Server