7.6 KiB
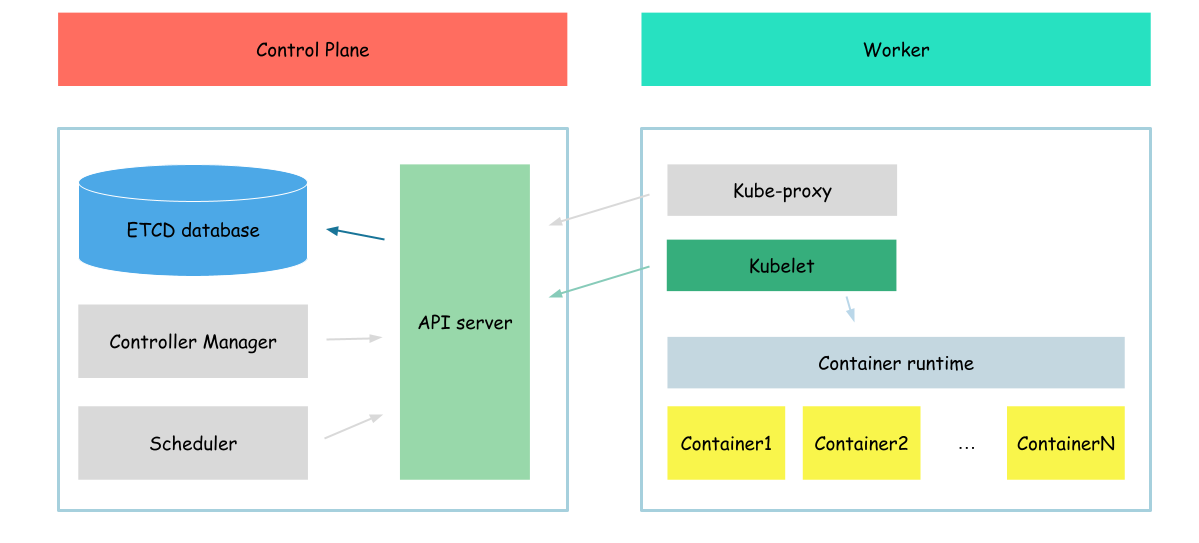
Apiserver - Kubelet integration
In this section, we will configure kubelet, to run not only static pods but also pods, created in API server.
certificates
Again we will start this part with the creation of the certificates which will be used by kubelet to communicate with api server, and also when api server will communicate with kubelet.
{
HOST_NAME=$(cat /etc/hostname)
cat <<EOF | tee kubelet-csr.json
{
"CN": "system:node:${HOST_NAME}",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "Portland",
"O": "system:nodes",
"OU": "Kubernetes The Hard Way",
"ST": "Oregon"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert \
-ca=ca.pem \
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
-config=ca-config.json \
-hostname=127.0.0.1,${HOST_NAME} \
-profile=kubernetes \
kubelet-csr.json | cfssljson -bare kubelet
}
Create certificates:
kubelet.csr
kubelet-key.pem
kubelet.pem
The most interesting configuration options:
- cn(common name) - value api server will use as a client name during authorization
- o(organozation) - user group api server will use during authorization
We specified "system:nodes" in the organization. It says api server that the client who uses which certificate belongs to the system:nodes group.
Now we need to distribute certificates generated.
cp kubelet-key.pem kubelet.pem /var/lib/kubelet/ \
&& cp ca.pem /var/lib/kubernetes/
service configuration
After certificates configured and distributed, we need to prepare configuration files for kubelet.
{
HOST_NAME=$(cat /etc/hostname)
kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--certificate-authority=ca.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--server=https://127.0.0.1:6443 \
--kubeconfig=kubelet.kubeconfig
kubectl config set-credentials system:node:${HOST_NAME} \
--client-certificate=kubelet.pem \
--client-key=kubelet-key.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--kubeconfig=kubelet.kubeconfig
kubectl config set-context default \
--cluster=kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--user=system:node:${HOST_NAME} \
--kubeconfig=kubelet.kubeconfig
kubectl config use-context default --kubeconfig=kubelet.kubeconfig
}
We created kubernetes configuration file, which says kubelet where api server is configured and chich certificates to use communicating with it
And now, move all our configuration settings to the proper folders
cp kubelet.kubeconfig /var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig
Also, we need to create KubeletConfiguration
cat <<EOF | tee /var/lib/kubelet/kubelet-config.yaml
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: true
webhook:
enabled: false
authorization:
mode: AlwaysAllow
networkPlugin: "cni"
cniConfDir: "/etc/cni/net.d"
cniBinDir: "/opt/cni/bin"
tlsCertFile: "/var/lib/kubelet/kubelet.pem"
tlsPrivateKeyFile: "/var/lib/kubelet/kubelet-key.pem"
EOF
Configuration options I want to highlight:
- podCIDR - the pod network cidr, the same as we configured previously
- tls configuration - certificate files which will be used by kubelet when api server connects to it
- authentication.webgook.enable - means that to authorize requests kubelet will ask api server
- cluster dns - the IP in which cluster DNS server will be hosted (more on this later)
And the last step - we need to update service configuration file
cat <<EOF | tee /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
After=containerd.service
Requires=containerd.service
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/kubelet \\
--container-runtime-endpoint=unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.sock \\
--file-check-frequency=10s \\
--config=/var/lib/kubelet/kubelet-config.yaml \\
--pod-manifest-path='/etc/kubernetes/manifests/' \\
--kubeconfig=/var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig \\
--register-node=true \\
--v=10
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
And reload it
systemctl daemon-reload \
&& systemctl enable kubelet \
&& systemctl restart kubelet
verification
And check service status
systemctl status kubelet
Output:
● kubelet.service - Kubernetes Kubelet
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-05-04 14:37:07 UTC; 11s ago
Docs: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
Main PID: 95898 (kubelet)
Tasks: 12 (limit: 2275)
Memory: 53.8M
CGroup: /system.slice/kubelet.service
└─95898 /usr/local/bin/kubelet --config=/var/lib/kubelet/kubelet-config.yaml --container-runtime=remote --container-runtime-endpoint=unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.soc>
...
After our kubelet is in running state, we can check if it is registered in API server
kubectl get nodes
Output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
example-server Ready <none> 1m2s v1.21.0
After our kubelet registered in API server we can check wheather our pod is in running state
kubectl get pod
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-world 1/1 Running 0 8m1s
As we can see out pod is in running state. In addition to this check we can also check if our pod is really in running state by using crictl Pods
crictl pods
Output:
POD ID CREATED STATE NAME NAMESPACE ATTEMPT RUNTIME
1719d0202a5ef 8 minutes ago Ready hello-world default 0 (default)
Also we can see logs from our pod
crictl logs $(crictl ps -q)
Output:
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
...
But now, lets view logs using kubectl instead of crictl. In our case it is maybe not very important, but in case of cluster with more than 1 node it is important, as crictl allows to read info only about pods on node, when kubectl (by communicating with api server) allows to read info from all nodes.
kubectl logs hello-world
Output:
Error from server (Forbidden): Forbidden (user=kubernetes, verb=get, resource=nodes, subresource=proxy) ( pods/log hello-world)
As we can see api server has no permissions to read logs from the node. This message apears, because during authorization, kubelet ask api server if the user with the name kubernetes has proper permission, but now it is not true. So let's fix this
{
cat <<EOF> node-auth.yml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: node-proxy-access
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes/proxy"]
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: node-proxy-access-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: node-proxy-access
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: User
name: kubernetes
EOF
kubectl apply -f node-auth.yml
}
After our cluster role and role binding creted we can retry
kubectl logs hello-world
Output:
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
...
As you can see, we can create pods and kubelet will run that pods.
Note: it takes some time to apply created RBAC policies.
Now, we need to clean-up out workspace.
kubectl delete -f pod.yaml
Check if pod deleted
kubectl get pod
Outpput:
No resources found in default namespace.
Next: Scheduler