7.4 KiB
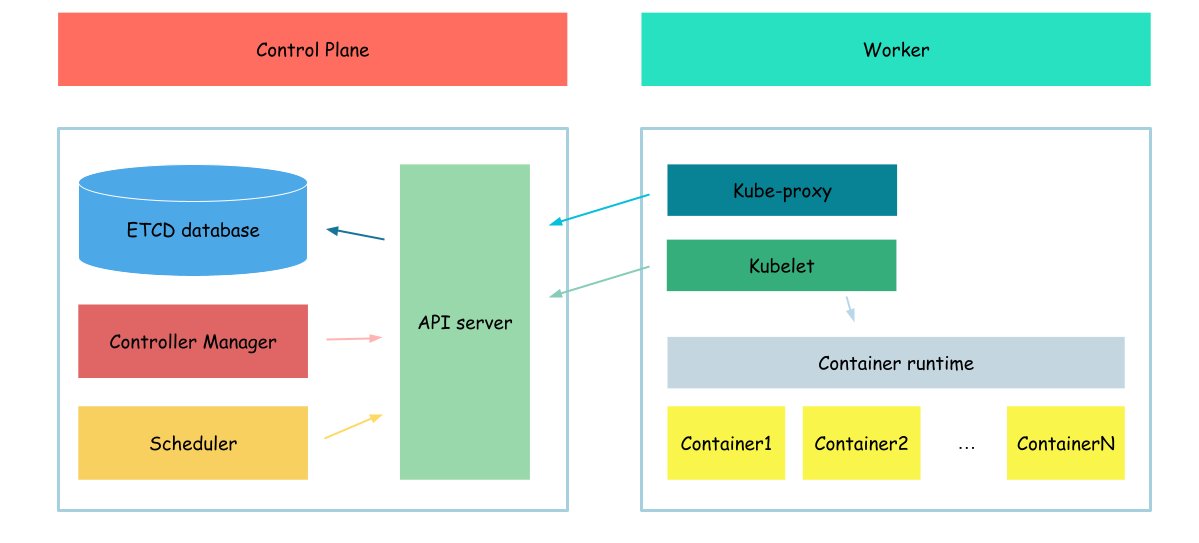
Kube-proxy
такс,
{
cat <<EOF> nginx-deployment.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-conf
data:
default.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
return 200 "Hello from pod: \$hostname\n";
}
}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.21.3
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-conf
mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d
volumes:
- name: nginx-conf
configMap:
name: nginx-conf
EOF
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yml
}
kubectl get pod -o wide
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-deployment-db9778f94-2zv7x 1/1 Running 0 63s 10.240.1.12 example-server <none> <none>
nginx-deployment-db9778f94-q5jx4 1/1 Running 0 63s 10.240.1.10 example-server <none> <none>
nginx-deployment-db9778f94-twx78 1/1 Running 0 63s 10.240.1.11 example-server <none> <none>
now, we will run busybox container and will try to access our pods from other container
{
cat <<EOF> pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busy-box
spec:
containers:
- name: busy-box
image: busybox
command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do echo "Busy"; sleep 1; done']
EOF
kubectl apply -f pod.yaml
}
and execute command from our container
kubectl exec busy-box -- wget -O - $(kubectl get pod -o wide | grep nginx | awk '{print $6}' | head -n 1)
Output:
error: unable to upgrade connection: Forbidden (user=kubernetes, verb=create, resource=nodes, subresource=proxy)
error occured because api server has no access to execute commands
{
cat <<EOF> rbac-create.yml
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: kubernetes-user-clusterrole
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes/proxy"]
verbs: ["create"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: kubernetes-user-clusterrolebinding
subjects:
- kind: User
name: kubernetes
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: kubernetes-user-clusterrole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
EOF
kubectl apply -f rbac-create.yml
}
and execute command from our container
kubectl exec busy-box -- wget -O - $(kubectl get pod -o wide | grep nginx | awk '{print $6}' | head -n 1)
Output:
Hello from pod: nginx-deployment-68b9c94586-qkwjc
Connecting to 10.32.0.230 (10.32.0.230:80)
writing to stdout
- 100% |********************************| 50 0:00:00 ETA
written to stdout
it is not very interesting to access pods by ip, we want to have some automatic load balancing we know that services may help us with that
{
cat <<EOF> nginx-service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
EOF
kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yml
}
get our server
kubectl get service
and try to ping our containers by service ip
kubectl exec busy-box -- wget -O - $(kubectl get service -o wide | grep nginx | awk '{print $3}')
Output:
Connecting to 10.32.0.230 (10.32.0.230:80)
hm, nothing happen, the reason - our cluster do not know how to connect to service ip
this is responsibiltiy of kube-proxy
it means that we need to configure kube-proxy
as usually we will start with certs
{
cat > kube-proxy-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "system:kube-proxy",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "Portland",
"O": "system:node-proxier",
"OU": "Kubernetes The Hard Way",
"ST": "Oregon"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert \
-ca=ca.pem \
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
-config=ca-config.json \
-profile=kubernetes \
kube-proxy-csr.json | cfssljson -bare kube-proxy
}
now connection config
{
kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--certificate-authority=ca.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--server=https://127.0.0.1:6443 \
--kubeconfig=kube-proxy.kubeconfig
kubectl config set-credentials system:kube-proxy \
--client-certificate=kube-proxy.pem \
--client-key=kube-proxy-key.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--kubeconfig=kube-proxy.kubeconfig
kubectl config set-context default \
--cluster=kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--user=system:kube-proxy \
--kubeconfig=kube-proxy.kubeconfig
kubectl config use-context default --kubeconfig=kube-proxy.kubeconfig
}
now, download kube-proxy
wget -q --show-progress --https-only --timestamping \
https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.21.0/bin/linux/amd64/kube-proxy
create proper folders
sudo mkdir -p \
/var/lib/kube-proxy
install binaries
{
chmod +x kube-proxy
sudo mv kube-proxy /usr/local/bin/
}
move connection config to proper folder
sudo mv kube-proxy.kubeconfig /var/lib/kube-proxy/kubeconfig
create kube-proxy config file
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /var/lib/kube-proxy/kube-proxy-config.yaml
kind: KubeProxyConfiguration
apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
clientConnection:
kubeconfig: "/var/lib/kube-proxy/kubeconfig"
mode: "iptables"
clusterCIDR: "10.200.0.0/16"
EOF
create kube-proxy service configufile
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/kube-proxy.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kube Proxy
Documentation=https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/kube-proxy \\
--config=/var/lib/kube-proxy/kube-proxy-config.yaml
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
start kube-proxy
{
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable kube-proxy
sudo systemctl start kube-proxy
}
and check its status
sudo systemctl status kube-proxy
Output:
● kube-proxy.service - Kubernetes Kube Proxy
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/kube-proxy.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-04-20 13:37:27 UTC; 23s ago
Docs: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
Main PID: 19873 (kube-proxy)
Tasks: 5 (limit: 2275)
Memory: 10.0M
CGroup: /system.slice/kube-proxy.service
└─19873 /usr/local/bin/kube-proxy --config=/var/lib/kube-proxy/kube-proxy-config.yaml
...
and now we can check the access to service ip once again
kubectl exec busy-box -- wget -O - $(kubectl get service -o wide | grep nginx | awk '{print $3}')
Hello from pod: nginx-deployment-68b9c94586-qkwjc
Connecting to 10.32.0.230 (10.32.0.230:80)
writing to stdout
- 100% |********************************| 50 0:00:00 ETA
written to stdout
if you try to repeat the command once again you will see that requests are handled by different pods
great we successfully configured kubeproxy and can balance trafic between containers
Next: DNS in Kubernetes